Debugging¶
Since xlwings runs in every Python environment, you can use your preferred way of debugging.
- RunPython: When calling Python through
RunPython, you can set amock_callerto make it easy to switch back and forth between calling the function from Excel and Python. - UDFs: For debugging User Defined Functions, xlwings offers a convenient debugging server
To begin with, Excel will show Python errors in a Message Box:
Note
On Mac, if the import of a module/package fails before xlwings is imported, the popup will not be shown and the StatusBar
will not be reset. However, the error will still be logged in the log file. For the location of the logfile, see Log File default locations.
RunPython¶
Consider the following sample code of your Python source code my_module.py:
# my_module.py
import os
import xlwings as xw
def my_macro():
wb = xw.Book.caller()
wb.sheets[0].range('A1').value = 1
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Expects the Excel file next to this source file, adjust accordingly.
xw.Book('myfile.xlsm').set_mock_caller()
my_macro()
my_macro() can now easily be run from Python for debugging and from Excel via RunPython without having to change the
source code:
Sub my_macro()
RunPython ("import my_module; my_module.my_macro()")
End Sub
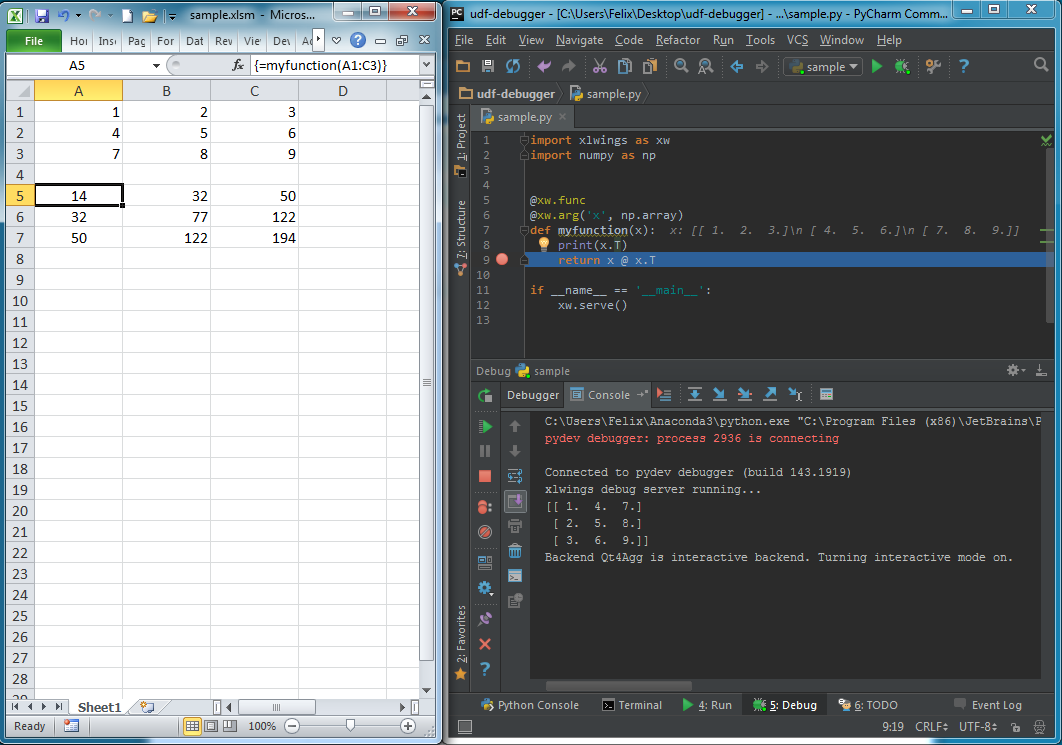
UDF debug server¶
Windows only: To debug UDFs, just check the Debug UDFs in the Add-in, at the top of the xlwings VBA module.
Then add the following lines at the end of your Python source file and run it. Depending on which IDE you use, you
might need to run the code in “debug” mode (e.g. in case you’re using PyCharm or PyDev):
if __name__ == '__main__':
xw.serve()
When you recalculate the Sheet (Ctrl-Alt-F9), the code will stop at breakpoints or output any print calls that you
may have.
The following screenshot shows the code stopped at a breakpoint in the community version of PyCharm:
Note
When running the debug server from a command prompt, there is currently no gracious way to terminate it, but closing the command prompt will kill it.