VBA: User Defined Functions (UDFs)¶
This tutorial gets you quickly started on how to write User Defined Functions.
Note
- UDFs are currently only available on Windows.
- For details of how to control the behaviour of the arguments and return values, have a look at Converters and Options.
- For a comprehensive overview of the available decorators and their options, check out the corresponding API docs: UDF decorators.
One-time Excel preparations¶
1) Enable Trust access to the VBA project object model under
File > Options > Trust Center > Trust Center Settings > Macro Settings
- Install the add-in via command prompt:
xlwings addin install(see Add-in).
Workbook preparation¶
The easiest way to start a new project is to run xlwings quickstart myproject on a command prompt (see Command Line Client).
This automatically adds the xlwings reference to the generated workbook.
A simple UDF¶
The default addin settings expect a Python source file in the way it is created by quickstart:
- in the same directory as the Excel file
- with the same name as the Excel file, but with a
.pyending instead of.xlsm.
Alternatively, you can point to a specific module via UDF Modules in the xlwings ribbon.
Let’s assume you have a Workbook myproject.xlsm, then you would write the following code in myproject.py:
import xlwings as xw
@xw.func
def double_sum(x, y):
"""Returns twice the sum of the two arguments"""
return 2 * (x + y)
Now click on
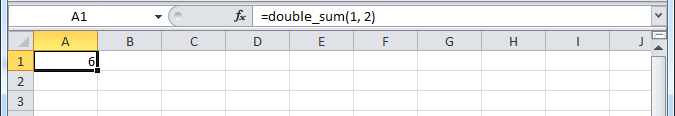
Import Python UDFsin the xlwings tab to pick up the changes made tomyproject.py.Enter the formula
=double_sum(1, 2)into a cell and you will see the correct result:The docstring (in triple-quotes) will be shown as function description in Excel.
Note
- You only need to re-import your functions if you change the function arguments or the function name.
- Code changes in the actual functions are picked up automatically (i.e. at the next calculation of the formula,
e.g. triggered by
Ctrl-Alt-F9), but changes in imported modules are not. This is the very behaviour of how Python imports work. If you want to make sure everything is in a fresh state, clickRestart UDF Server. - The
@xw.funcdecorator is only used by xlwings when the function is being imported into Excel. It tells xlwings for which functions it should create a VBA wrapper function, otherwise it has no effect on how the functions behave in Python.
Array formulas: Get efficient¶
Calling one big array formula in Excel is much more efficient than calling many single-cell formulas, so it’s generally a good idea to use them, especially if you hit performance problems.
You can pass an Excel Range as a function argument, as opposed to a single cell and it will show up in Python as list of lists.
For example, you can write the following function to add 1 to every cell in a Range:
@xw.func
def add_one(data):
return [[cell + 1 for cell in row] for row in data]
To use this formula in Excel,
- Click on
Import Python UDFsagain - Fill in the values in the range
A1:B2 - Select the range
D1:E2 - Type in the formula
=add_one(A1:B2) - Press
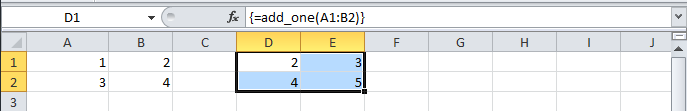
Ctrl+Shift+Enterto create an array formula. If you did everything correctly, you’ll see the formula surrounded by curly braces as in this screenshot:
Number of array dimensions: ndim¶
The above formula has the issue that it expects a “two dimensional” input, e.g. a nested list of the form
[[1, 2], [3, 4]].
Therefore, if you would apply the formula to a single cell, you would get the following error:
TypeError: 'float' object is not iterable.
To force Excel to always give you a two-dimensional array, no matter whether the argument is a single cell, a column/row or a two-dimensional Range, you can extend the above formula like this:
@xw.func
@xw.arg('data', ndim=2)
def add_one(data):
return [[cell + 1 for cell in row] for row in data]
Array formulas with NumPy and Pandas¶
Often, you’ll want to use NumPy arrays or Pandas DataFrames in your UDF, as this unlocks the full power of Python’s ecosystem for scientific computing.
To define a formula for matrix multiplication using numpy arrays, you would define the following function:
import xlwings as xw
import numpy as np
@xw.func
@xw.arg('x', np.array, ndim=2)
@xw.arg('y', np.array, ndim=2)
def matrix_mult(x, y):
return x @ y
Note
If you are not on Python >= 3.5 with NumPy >= 1.10, use x.dot(y) instead of x @ y.
A great example of how you can put Pandas at work is the creation of an array-based CORREL formula. Excel’s
version of CORREL only works on 2 datasets and is cumbersome to use if you want to quickly get the correlation
matrix of a few time-series, for example. Pandas makes the creation of an array-based CORREL2 formula basically
a one-liner:
import xlwings as xw
import pandas as pd
@xw.func
@xw.arg('x', pd.DataFrame, index=False, header=False)
@xw.ret(index=False, header=False)
def CORREL2(x):
"""Like CORREL, but as array formula for more than 2 data sets"""
return x.corr()
@xw.arg and @xw.ret decorators¶
These decorators are to UDFs what the options method is to Range objects: they allow you to apply converters and their
options to function arguments (@xw.arg) and to the return value (@xw.ret). For example, to convert the argument x into
a pandas DataFrame and suppress the index when returning it, you would do the following:
@xw.func
@xw.arg('x', pd.DataFrame)
@xw.ret(index=False)
def myfunction(x):
# x is a DataFrame, do something with it
return x
For further details see the Converters and Options documentation.
Dynamic Array Formulas¶
As seen above, to use Excel’s array formulas, you need to specify their dimensions up front by selecting the
result array first, then entering the formula and finally hitting Ctrl-Shift-Enter. While this makes sense from
a data integrity point of view, in practice, it often turns out to be a cumbersome limitation, especially when working
with dynamic arrays such as time series data. Since v0.10, xlwings offers dynamic UDF expansion:
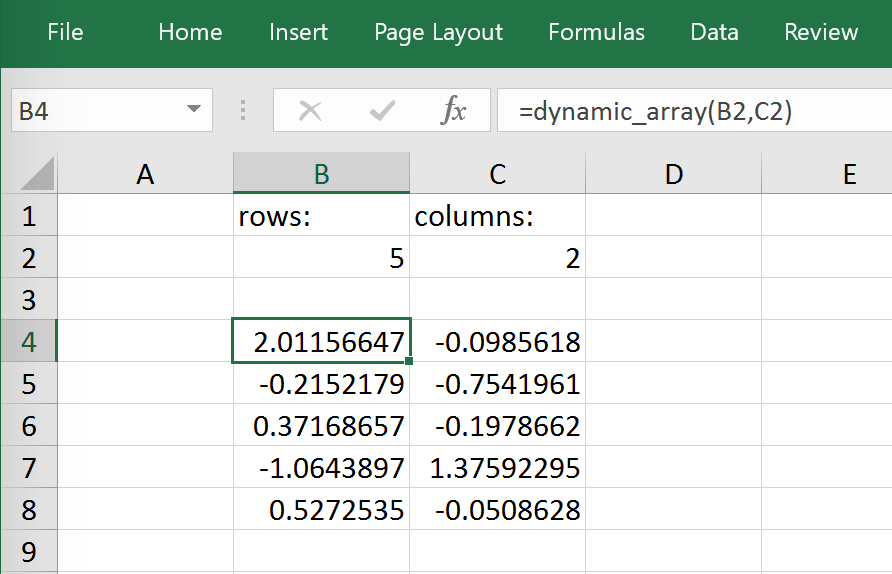
This is a simple example that demonstrates the syntax and effect of UDF expansion:
import numpy as np
@xw.func
@xw.ret(expand='table')
def dynamic_array(r, c):
return np.random.randn(int(r), int(c))
Note
- Expanding array formulas will overwrite cells without prompting and leave an empty border around them, i.e. they will clear the row to the bottom and the column to the right of the array.
- The way that dynamic array formulas are currently implemented doesn’t allow them to have volatile functions
as arguments, e.g. you cannot use functions like
=TODAY()as arguments.
Docstrings¶
The following sample shows how to include docstrings both for the function and for the arguments x and y that then show up in the function wizard in Excel:
import xlwings as xw
@xw.func
@xw.arg('x', doc='This is x.')
@xw.arg('y', doc='This is y.')
def double_sum(x, y):
"""Returns twice the sum of the two arguments"""
return 2 * (x + y)
The “vba” keyword¶
It’s often helpful to get the address of the calling cell. Right now, one of the easiest ways to
accomplish this is to use the vba keyword. vba, in fact, allows you to access any available VBA expression
e.g. Application. Note, however, that currently you’re acting directly on the pywin32 COM object:
@xw.func
@xw.arg('xl_app', vba='Application')
def get_caller_address(xl_app):
return xl_app.Caller.Address
Macros¶
On Windows, as alternative to calling macros via RunPython, you can also use the @xw.sub
decorator:
import xlwings as xw
@xw.sub
def my_macro():
"""Writes the name of the Workbook into Range("A1") of Sheet 1"""
wb = xw.Book.caller()
wb.sheets[0].range('A1').value = wb.name
After clicking on Import Python UDFs, you can then use this macro by executing it via Alt + F8 or by
binding it e.g. to a button. To to the latter, make sure you have the Developer tab selected under File >
Options > Customize Ribbon. Then, under the Developer tab, you can insert a button via Insert > Form Controls.
After drawing the button, you will be prompted to assign a macro to it and you can select my_macro.
Call UDFs from VBA¶
Imported functions can also be used from VBA. They return a 2d array:
Sub MySub()
Dim arr() As Variant
Dim i As Long, j As Long
arr = my_imported_function(...)
For j = LBound(arr, 2) To UBound(arr, 2)
For lRow = LBound(arr, 1) To UBound(arr, 1)
Debug.Print "(" & i & "," & j & ")", arr(i, j)
Next i
Next j
End Sub